When it comes to electrical wiring, understanding the different types of outlets and their wiring diagrams is crucial. One common type is the 220v 3 prong outlet, which is commonly used for heavy-duty appliances such as dryers and stoves. Knowing how to correctly wire these outlets can ensure safety and proper functionality.
It is important to note that working with electricity can be dangerous, so if you are not confident in your abilities, it is best to hire a professional electrician to do the job. However, if you have some knowledge and experience in electrical work, understanding the wiring diagram for a 220v 3 prong outlet can be useful.
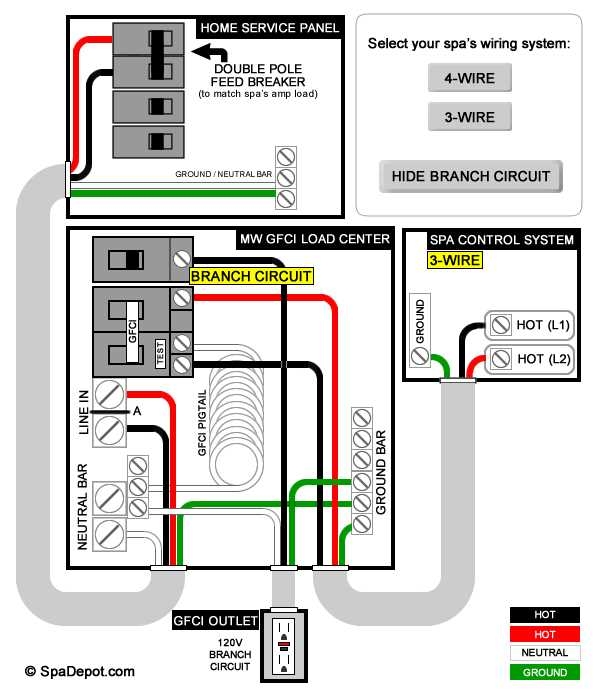 220v 3 Prong Outlet Wiring Diagram
220v 3 Prong Outlet Wiring Diagram
220v 3 Prong Outlet Wiring Diagram
The wiring diagram for a 220v 3 prong outlet consists of three wires – a hot wire, a neutral wire, and a ground wire. The hot wire carries the electrical current from the circuit breaker to the outlet, the neutral wire completes the circuit back to the breaker, and the ground wire provides a path for electrical currents in case of a fault.
When wiring a 220v 3 prong outlet, the hot wire is typically connected to one of the two brass screws on the outlet, the neutral wire is connected to the silver screw, and the ground wire is connected to the green screw. It is important to ensure that the wires are securely connected and that there are no loose connections that could cause a short circuit.
Before attempting to wire a 220v 3 prong outlet, it is important to turn off the power at the circuit breaker and double-check that the power is off using a voltage tester. Once the outlet is wired correctly, it can be tested using a multimeter to ensure that it is functioning properly.
In conclusion, understanding the wiring diagram for a 220v 3 prong outlet is important for anyone working with electrical appliances. By following the proper procedures and safety precautions, you can ensure that your outlet is wired correctly and safely. If in doubt, always seek the help of a professional electrician to avoid any potential hazards.